Understanding Cultural Relativism: A Deep Dive into Cultural Understanding
When we look at the world around us, we see a vast tapestry of cultures, each with its own unique beliefs, values, and practices. Cultural relativism is a concept that helps us make sense of this diversity by encouraging us to approach other cultures with an open mind and without judgment. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of cultural relativism, its significance in today’s globalized world, and how it can shape our perceptions of the world we live in.
The Roots of Cultural Relativism

Cultural relativism is a concept that has its roots in anthropology, the study of human societies and cultures. The idea was first popularized by Franz Boas, known as the “father of American anthropology,” in the early 20th century. Boas believed that in order to truly understand a culture, one must immerse oneself in it and view it from the perspective of its members. This approach was a radical departure from the ethnocentric views that prevailed at the time, which judged other cultures based on the standards of one’s own.
One of the key principles of cultural relativism is that there are no universal standards for judging cultures. What may be considered normal or acceptable in one culture may be frowned upon or even taboo in another. This idea challenges us to question our own beliefs and values, and to consider that there are multiple ways of understanding and interpreting the world.
For example, in some cultures, it is customary to greet others with a kiss on the cheek, while in others, a firm handshake is more appropriate. In some societies, it is common for extended families to live together under one roof, while in others, independence and individualism are prized. These differences may seem trivial, but they reflect deeper cultural norms and values that shape how people interact with one another and understand the world around them.
Cultural Relativism in Practice

Understanding cultural relativism is not just an academic exercise; it has real-world implications for how we interact with others and navigate the complexities of a globalized world. In today’s interconnected society, we are more likely than ever to encounter people from different cultural backgrounds, whether in our own communities or through travel and social media.
One of the key benefits of cultural relativism is that it promotes empathy and understanding between people of different cultures. By recognizing that our own cultural norms are not the only valid ones, we can foster greater respect and appreciation for the diversity of human experience. This can help bridge divides and build connections between people who might otherwise see each other as “other.”
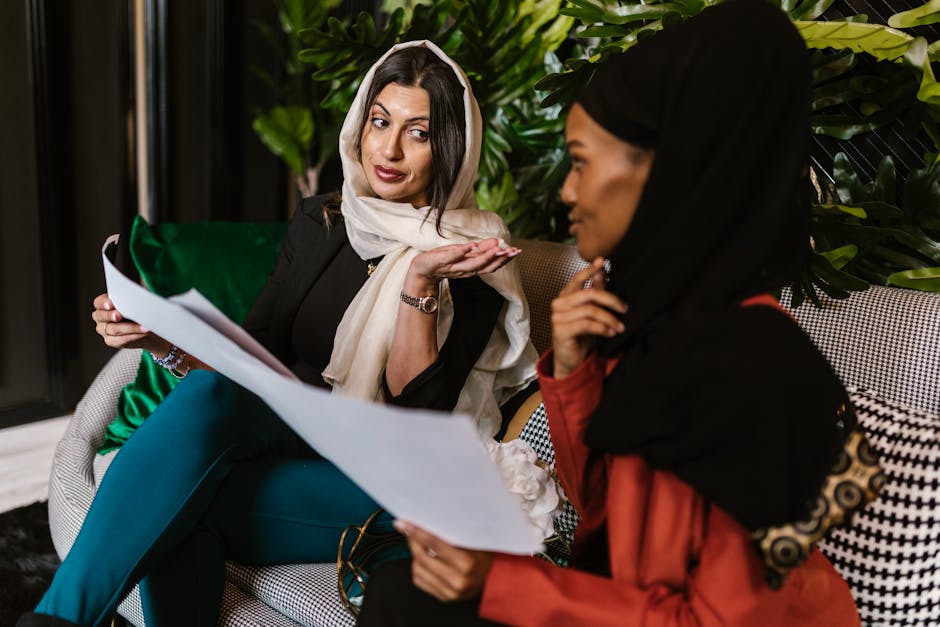
For example, consider the practice of wearing headscarves in some Muslim cultures. In Western societies, this practice is often misunderstood or criticized as oppressive to women. However, from a cultural relativist perspective, we can see that wearing a headscarf can be a symbol of religious devotion, modesty, or cultural identity. By reframing our understanding in this way, we can begin to appreciate the complexity and nuance of different cultural practices.
Another important aspect of cultural relativism is its impact on human rights and social justice. Critics of cultural relativism argue that it can lead to moral relativism, the idea that there are no universal moral truths and that all beliefs and practices are equally valid. This can be a slippery slope, as it may justify harmful practices such as female genital mutilation or child marriage in the name of cultural tradition.
However, cultural relativism does not mean that all cultural practices are morally equivalent or beyond critique. It simply asks us to approach other cultures with humility and respect, recognizing that our own perspectives are not the only ones that matter. By engaging in dialogue and debate with members of other cultures, we can work towards a more just and equitable world that respects the dignity and rights of all individuals.
Challenges and Controversies

While cultural relativism offers a valuable framework for understanding and appreciating cultural diversity, it is not without its challenges and controversies. One of the main criticisms of cultural relativism is that it can lead to moral relativism, as mentioned earlier. Some argue that if all cultural practices are considered equally valid, then there is no basis for critiquing harmful practices or advocating for human rights.
Another criticism is that cultural relativism can be used as a shield to protect oppressive or discriminatory practices in the name of cultural tradition. For example, some argue that certain cultural practices, such as honor killings or caste discrimination, should be condemned universally, regardless of cultural context. In these cases, cultural relativism can be seen as a form of moral relativism that prioritizes cultural authenticity over human rights.
Additionally, cultural relativism can sometimes be taken to an extreme, where any attempt to critique or challenge cultural practices is seen as ethnocentric or imperialistic. This can stifle meaningful dialogue and prevent constructive engagement with other cultures, leading to misunderstandings and conflicts.
Despite these challenges, cultural relativism remains a valuable tool for promoting intercultural understanding and empathy. By approaching other cultures with an open mind and a willingness to learn, we can break down stereotypes, build bridges of communication, and foster a sense of global community.
Common Misconceptions

One common misconception about cultural relativism is that it requires us to abandon our own cultural values and beliefs in favor of those of other cultures. In reality, cultural relativism does not ask us to give up our own values, but rather to recognize that others may hold different values that are equally valid within their cultural context.
Another misconception is that cultural relativism promotes moral relativism, the idea that all moral beliefs are subjective and there are no universal standards of right and wrong. While cultural relativism does challenge us to question our own moral assumptions and consider the perspectives of others, it does not mean that all moral beliefs are equally valid or beyond critique.
Ultimately, cultural relativism is about approaching other cultures with humility, curiosity, and respect, recognizing that diversity is a strength and that there is much we can learn from engaging with people who see the world differently from us.
FAQs
1. How does cultural relativism differ from ethnocentrism?
Cultural relativism is the belief that all cultures are equally valid and should be understood on their own terms, without judgment. Ethnocentrism, on the other hand, is the tendency to view one’s own culture as superior to others and to judge other cultures based on one’s own standards.
2. Does cultural relativism mean that all cultural practices are acceptable?
No, cultural relativism does not mean that all cultural practices are acceptable. It simply asks us to approach other cultures with an open mind and a willingness to learn, recognizing that our own perspectives are not the only ones that matter.
3. How can I practice cultural relativism in my daily life?
One way to practice cultural relativism in your daily life is to approach encounters with people from different cultures with an open mind and a willingness to listen. Ask questions, seek to understand, and be respectful of cultural differences.
To Wrap Things Up
In conclusion, cultural relativism is a powerful concept that challenges us to see the world through the eyes of others, to appreciate the richness and diversity of human experience, and to engage with empathy and understanding across cultural divides. By embracing cultural relativism, we can break down barriers, build connections, and create a more inclusive and harmonious world for all.