The Role of Art in Social Change
Art has been a powerful form of expression, reflection, and communication for centuries. Beyond its aesthetic appeal, art has the ability to provoke thought, incite emotions, and inspire action. In the realm of social change, art plays a crucial role in shaping attitudes, challenging norms, and advocating for justice. From visual arts to performing arts, literature to music, art has the unique ability to transcend language barriers and connect people from diverse backgrounds.
How does art influence social change? What makes art such a potent tool for activism and advocacy? In this article, we delve into the multifaceted role of art in driving social change, exploring its historical significance, current applications, and future potential. Join us on a journey through the intersection of art and activism, where creativity becomes a catalyst for transforming society.
The Power of Visual Arts
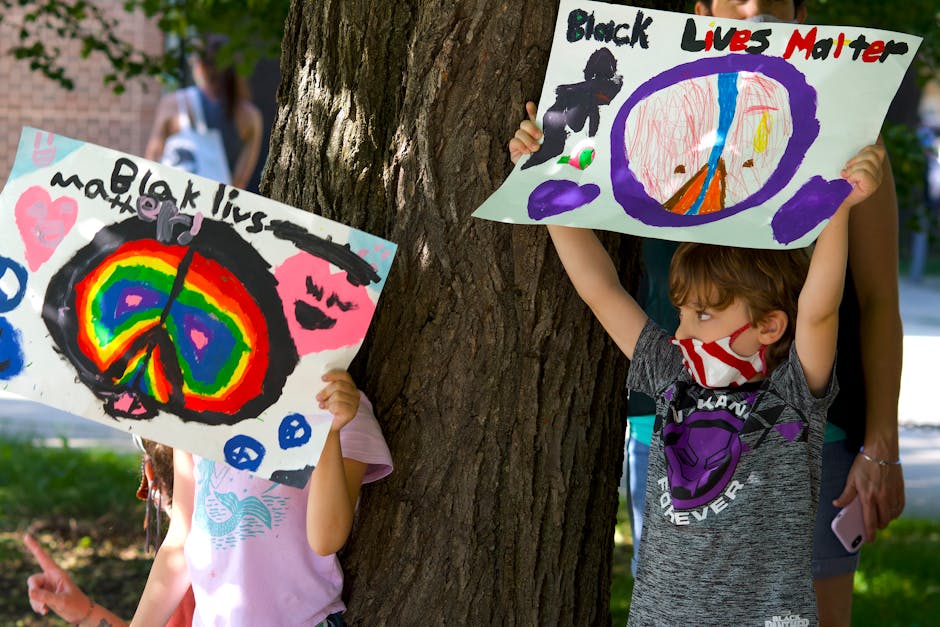
The visual arts, including painting, sculpture, photography, and street art, have long been vehicles for social commentary and political critique. Artists throughout history have used their medium to shed light on social injustices, amplify marginalized voices, and challenge the status quo. One prominent example is the Guernica painting by Pablo Picasso, which vividly depicts the horrors of the Spanish Civil War and serves as a timeless symbol of anti-war activism.
Contemporary artists continue to engage with pressing social issues through their work. For instance, the Black Lives Matter movement has inspired a wave of powerful artworks that address systemic racism, police brutality, and racial inequality. Artists like Kara Walker, Kehinde Wiley, and Banksy have brought attention to these issues through their provocative and thought-provoking pieces.
The Role of Performing Arts

Performing arts, including theater, dance, and music, have the ability to engage audiences in a visceral and emotional way. Stage performances, dance routines, and musical compositions can convey powerful messages, evoke empathy, and spark conversations about social issues. For example, the Broadway musical “Hamilton” reimagines the founding of America through a diverse and inclusive lens, challenging traditional narratives and celebrating the contributions of people of color.
Dance movements like “flash mobs” and “protest dances” have become popular forms of protest and social activism. By choreographing routines in public spaces, dancers can draw attention to specific causes, raise awareness, and mobilize communities. Dance has the unique ability to break down barriers, unite people, and create a sense of shared purpose.
Literature as a Catalyst for Change

Literature, including novels, poetry, essays, and spoken word, has the power to challenge perceptions, spark dialogue, and inspire change. Writers throughout history have used their words to advocate for social justice, human rights, and equality. From Harriet Beecher Stowe’s “Uncle Tom’s Cabin” to Maya Angelou’s “I Know Why the Caged Bird Sings,” literature has the ability to educate, empower, and transform minds.
Contemporary authors continue to address pressing social issues through their writing. Books like “The Hate U Give” by Angie Thomas, “Just Mercy” by Bryan Stevenson, and “We Should All Be Feminists” by Chimamanda Ngozi Adichie have become essential reading for those seeking to understand and engage with social change movements. Literature has the power to amplify diverse voices, challenge dominant narratives, and inspire empathy.
Music as a Tool for Advocacy

Music has the ability to transcend cultural boundaries, evoke emotions, and unite communities. Musicians have long used their songs as a form of protest, resistance, and solidarity. From protest songs during the civil rights movement to anthems of empowerment in the feminist movement, music has played a vital role in social change efforts.
Artists like Bob Dylan, Nina Simone, and John Lennon have used their music to address issues of war, racism, and social inequality. More recently, artists like Beyonc, Kendrick Lamar, and Janelle Mone have used their platforms to advocate for racial justice, gender equality, and LGBTQ rights. Music has the power to inspire, motivate, and mobilize individuals to take action.
The Intersection of Art and Technology
In the digital age, technology has provided new avenues for artists to create, share, and engage with audiences around the world. Social media platforms, online galleries, and virtual reality experiences have transformed the way art is produced and consumed. Artists can now reach a global audience with the click of a button, spreading their message far and wide.
Online activism, or “clicktivism,” has become a powerful tool for social change, allowing artists to mobilize supporters, raise awareness, and fundraise for important causes. Crowdfunding platforms like Kickstarter and GoFundMe have enabled artists to finance their projects independently, without relying on traditional gatekeepers. Technology has democratized the art world, making it more accessible and inclusive.
The Role of Art Institutions
Art institutions, including museums, galleries, and cultural centers, play a pivotal role in shaping public discourse, preserving history, and promoting social change. These institutions serve as spaces for dialogue, reflection, and education, inviting visitors to engage with art in a meaningful way. Curators, educators, and artists collaborate to curate exhibitions, organize events, and develop programming that addresses pressing social issues.
Many art institutions have taken steps to diversify their collections, highlight underrepresented artists, and foster inclusive spaces for dialogue. Initiatives like the “Decolonize This Place” movement and the “Museum As Site for Social Action” project seek to challenge colonial legacies, amplify marginalized voices, and promote equity in the art world. Art institutions have the power to shape narratives, challenge assumptions, and inspire change.
Art as a Form of Healing and Resistance
Art has the ability to heal, empower, and uplift individuals and communities. In times of crisis, trauma, or injustice, art can serve as a form of resistance, resilience, and renewal. Art therapy, community murals, and public installations provide spaces for self-expression, reflection, and solidarity.
Groups like the “Artivist Collective” and the “Guerilla Girls” use art as a form of activism, blending creative expression with social justice advocacy. By creating art that challenges dominant narratives, empowers marginalized voices, and demands systemic change, these artists inspire others to join the fight for a more just and equitable world. Art can be a powerful tool for healing wounds, building connections, and fostering empathy.
Expert Opinions
According to renowned artist and activist Ai Weiwei, “Art is not a handicraft, it is the transmission of feeling the artist has experienced.” Ai Weiwei’s work often addresses human rights abuses, government censorship, and social justice issues, using art as a form of protest and advocacy. His provocative installations, sculptures, and documentaries challenge viewers to confront uncomfortable truths and engage with urgent social issues.
Art historian and curator Kimberly Drew emphasizes the importance of representation and diversity in the art world, stating, “Art has the power to shape culture, challenge perceptions, and amplify unheard voices. When we support and celebrate diverse artists, we create a more inclusive and equitable society.” Drew’s work focuses on promoting artists of color, LGBTQ artists, and other underrepresented voices in the art world, advocating for greater representation and visibility.
Common Misconceptions
One common misconception about art in social change is that it is only effective in certain contexts or for specific audiences. In reality, art has the power to reach people across cultural, linguistic, and geographical boundaries, sparking conversations and inspiring action. Whether through a powerful painting, a moving performance, or a stirring poem, art has the ability to connect individuals from diverse backgrounds and mobilize them around shared values.
Another misconception is that art is separate from politics or activism. In truth, art has always been intertwined with social movements, political struggles, and advocacy efforts. Artists have long used their creativity to challenge authority, question norms, and demand justice. From the feminist art movement of the 1970s to the environmental art movement of the 21st century, art has been a potent tool for change.
Conclusion
Art is more than just a form of expression; it is a powerful force for social change. From visual arts to performing arts, literature to music, art has the ability to shape attitudes, challenge norms, and advocate for justice. By engaging with pressing social issues, amplifying marginalized voices, and inspiring empathy, art has the capacity to transform society, one brushstroke, one dance move, one verse at a time.
As we navigate complex challenges like climate change, racial inequality, and global pandemics, art offers us a way to process, reflect, and respond to the world around us. By harnessing the power of creativity, imagination, and collaboration, we can harness the transformative potential of art to envision a more just, equitable, and sustainable future for all.
Long story short, the role of art in social change is not just about aesthetics; it is about activism, advocacy, and amplification. Let us embrace the power of art to inspire change, challenge injustice, and create a better world for generations to come.




